Are you interested in the stock market but not sure what a bull or bear market is? This article will provide an overview of what these terms mean and how they can affect your investments. A bull market is a period of financial optimism during which investors are confident about the future and stock prices consistently rise. Conversely, a bear market describes a period of financial pessimism where investors expect prices to fall and sell their stocks. Understanding these two terms is essential for success in any stock market venture.
Bull Market
A bull market occurs when investor confidence is high, and prices rise across asset classes such as stocks, bonds, and real estate. This type of market is often characterized by optimism for the future and increased investor activity. During a bull market, stock prices will generally trend upward over time due to rising demand from buyers who believe that assets are undervalued or have the potential for long-term growth.
In addition to buying stocks, investors may also look to other investment vehicles like bonds or real estate during a bull market. Bonds typically become more attractive in this market because they offer higher yields than riskier investments like stocks. Real estate can also be attractive as low-interest rates make mortgages more affordable and increase the potential for capital appreciation. As such, a bull market fosters greater investment in both traditional securities and alternative asset classes alike.
Positive economic data, such as low unemployment or high consumer confidence, can incentivize investors to buy into the stock market. This creates investor demand for stocks and drives up their prices. Additionally, beneficial government policies such as tax cuts or deregulation can also increase investor confidence in the stock market and lead to higher prices.
Finally, technological advancements in industries like artificial intelligence or biotechnology can create new markets with huge potential profits for investors. Innovations allow companies to develop new products and services quickly while capturing large shares of the global marketplace, which will result in rising stock prices during a bull market.
Bear Market
Falling prices, reduced investor confidence, and a negative outlook characterize a bear market. Stocks, bonds, and real estate markets tend to decrease in value during a bear market due to the pessimism held by investors. This pessimistic sentiment leads to lower demand for securities as investors fear incurring losses. As a result, more sellers enter the market, further contributing to decreased prices across all asset classes.
The impact of a bear market can be felt throughout the economy as consumer spending decreases due to lower confidence in their financial situations. Companies may also suffer from reduced sales leading them to cut costs such as employee salaries or layoffs to remain profitable. Furthermore, companies may be forced into bankruptcy if their assets become worth less than their liabilities as stockholders refuse to purchase shares at low prices.
Bear markets can be caused by various factors, such as economic recessions, increased market volatility, decreased consumer confidence, and political instability. When an economy enters a recession, it stresses the stock market. As businesses struggle to make profits during difficult economic times, their stocks take hits, and markets drop significantly. Moreover, investors become skittish when there is increased uncertainty due to political turbulence or high levels of volatility in the financial markets. They tend to sell off their stocks at rapid rates. This leads to further declines in the stock market that result in an overall bearish sentiment among traders.
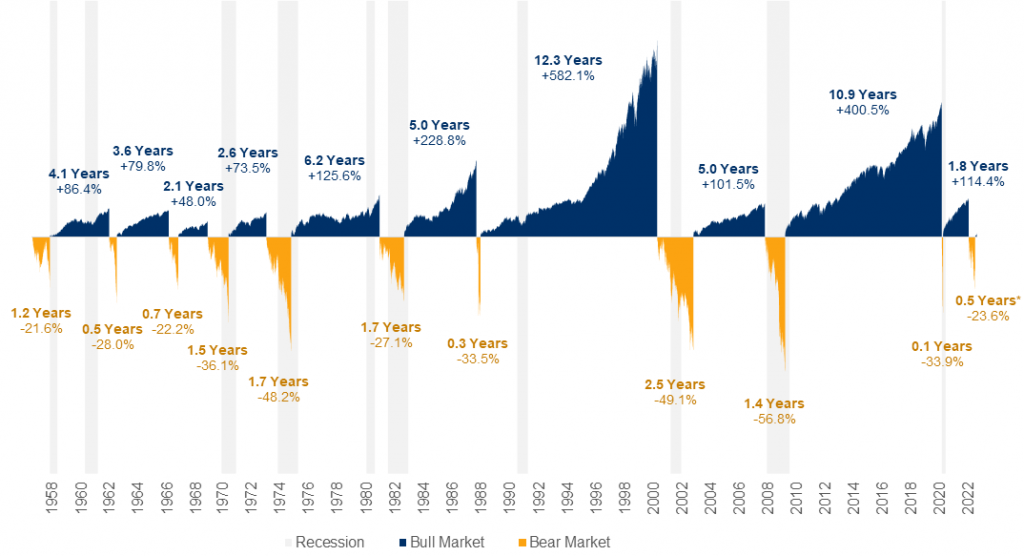
Credit: rbcgam.com
Factors affecting Bull and Bear Market
Economic indicators
Economic indicators such as Gross Domestic Product (GDP), inflation, and employment rates can significantly impact the stock market’s bull and bear cycles. Knowing how these metrics correlate with the markets can help investors understand when to buy or sell assets. The GDP is an indicator of economic growth that measures a nation’s overall production. When GDP increases, it usually means an increase in consumer spending, investment, and government spending that leads to economic expansion and positively impacts stock prices. Similarly, low unemployment rates are seen as positive signs for the economy because workers have access to higher wages leading to increased spending power that stimulates consumption and drives market growth. In contrast, high inflation hurts consumers because their purchasing power declines while producers benefit from rising prices which could be reflected in increased share value.
Political events
Political events such as elections, changes in government policies, or geopolitical tensions can have a significant impact on both bull and bear markets. For example, an election victory for a party with plans to reduce taxes could lead to increased risk-taking among investors as they eagerly anticipate future gains. This might result in a bullish market with rising stock prices and increased trading volumes. Conversely, political uncertainty due to ongoing trade wars or disagreements between countries could cause investors to become more cautious and pull back from investments in the stock market leading to bearish conditions.
Technological advancements
Introducing new technologies can majorly impact the markets, resulting in either a bull or bear market. Technological advancements create growth opportunities, leading to what is known as a bull market. On the other hand, technological disruptions can cause a bear market to emerge. Investor sentiment and business confidence may suffer during these times as investors become wary of the future prospects for the economy or industry outlooks. Furthermore, companies may face increasing competition from new entrants with disruptive technologies that challenge traditional business methods.
Investment Strategies for Bull and Bear Market
Typical bull market strategy
During a bull market, the economy grows and prospers, where stock prices climb steadily over a prolonged period. Investors in these times have an opportunity to maximize their returns by investing in growth-oriented assets such as stocks and real estate. This strategy involves taking on more risk than would be the case during a bear market when safer investments such as bonds or cash may be preferred.
One way to invest during a bull market is to look for undervalued stocks poised to take off with the rising economy. Identifying sectors that will benefit from the current trends can help investors spot those companies that have the potential for significant gains if conditions remain favorable. Additionally, investing in real estate can provide investors with long-term capital appreciation and rental income from tenants if properties are bought at the right price points.
Typical bear market strategy
A bear market is a period of time when stock prices are falling and investors may experience losses if they do not adjust their strategies accordingly. During such economic downturns, the best way to reduce risk is by diversifying your investments and focusing on safer assets such as bonds and cash rather than stocks. Investors should also consider selling off certain stocks that have dropped in value during the bear market. This can be beneficial because it will help decrease potential losses while allowing them to invest in other assets that may yield better returns once the economy recovers. As an additional precaution, investors should avoid investing in speculative securities or high-risk investments – instead focusing on more conservative options including government bonds and certificates of deposit (CDs).