Inflation affects all investments, but how it does so varies depending on the type of investment. Understanding the impact of inflation on investments will help you decide what investments offer attractive returns for your current financial goals. Inflation can erode the purchasing power of any investment—or even an entire portfolio—if not properly managed.
Put simply, inflation refers to the year-over-year rise in prices that erode the purchasing power of any given currency. All investment types involve some amount of speculation regarding future inflation or deflation and use various methods to help manage and protect against it. As a result, investors should take into account current economic trends when investing.
It is also vital to consider taxation implications—such as capital gains taxes—as these can significantly affect the overall investment return. Evaluating inflation and taxation allows investors to determine which strategies best suit their unique financial situation and objectives in life.
In this guide, we will discuss how inflation affects different types of investments and how investors can use knowledge about each investment type’s relationship with inflation to make sound financial decisions.
Understanding Inflation
Inflation can affect people’s purchasing power and investments, leading to more significant financial risks.
Understanding inflation is particularly important for investors as it dramatically impacts their returns. Inflation erodes the value of cash and can cause investments to lose value over time, reducing profits over the long run. It can also increase market volatility, particularly when inflation rises too quickly during economic uncertainty.
Therefore, individuals need to consider inflation when planning for retirement or other long-term goals involving investing capital for future use. Knowing historical inflation rate trends will help them make more proper decisions about investment strategies suitable for their situation and risk profile. This knowledge can also help inform appropriate asset allocation and determine whether or not they should hedge against potential adverse effects of inflation through various products offered by brokerages or certain investment firms such as hedge funds.
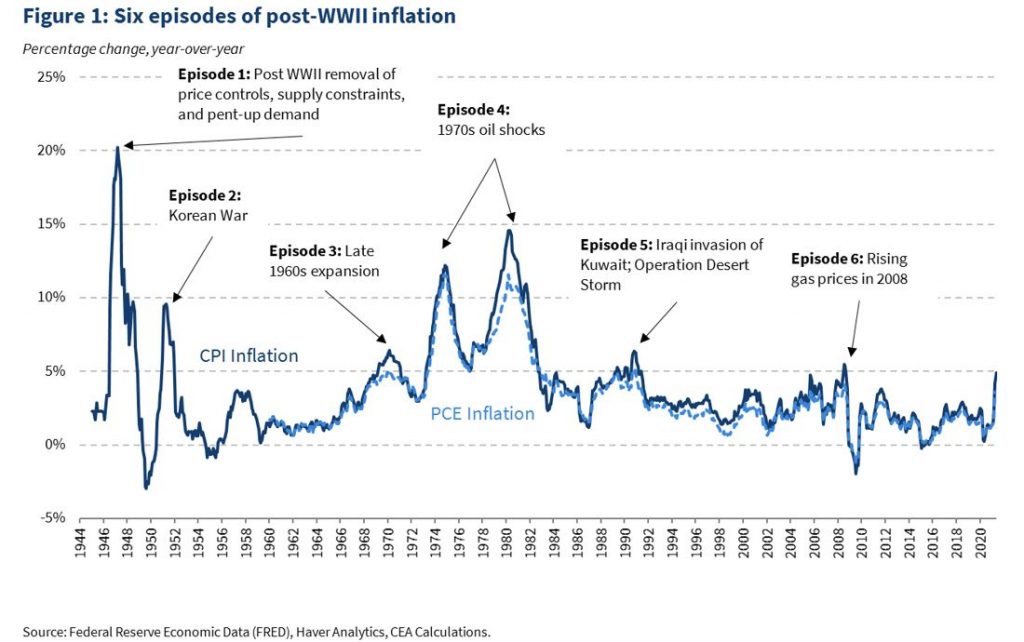
Credit: whitehouse.gov
Inflation and Investment Strategies
Inflation can affect various types of investments differently due to their sensitivity to changes in interest rates or prices for securities or commodities within a portfolio. For example, stocks may benefit from increased company profits associated with higher prices caused by inflation. In contrast, debt instruments like bonds may be hurt as rising interest rates increase their cost of borrowing from the market. In addition, high inflation often motivates investors to pursue safe-haven assets such as gold or government bonds as a hedge against currency depreciation and increases in overall market volatility.
Investment strategies can also help investors mitigate the impact of inflation on their portfolios by balancing risk/return objectives through diversification and asset allocation techniques and actively managing exposure to volatile markets. Diversification across asset classes helps protect against large fluctuations due to unanticipated market events. In contrast, prudent asset allocation enables optimal exposure to securities that profit from higher prices while keeping an adequate cushion against losses caused by rising real interest rates. Other popular methods involve utilizing tax efficiencies such as municipal bonds or real estate investment trusts (REITs) which offer tax advantages only when similar holdings are not found within mutual funds or ETFs.
In conclusion, inflation significantly impacts investments, and investing strategies should be chosen accordingly to best capitalize on weakening currency values while minimizing risks associated with unexpected market changes resulting from high rates of price increase throughout an economy over time.
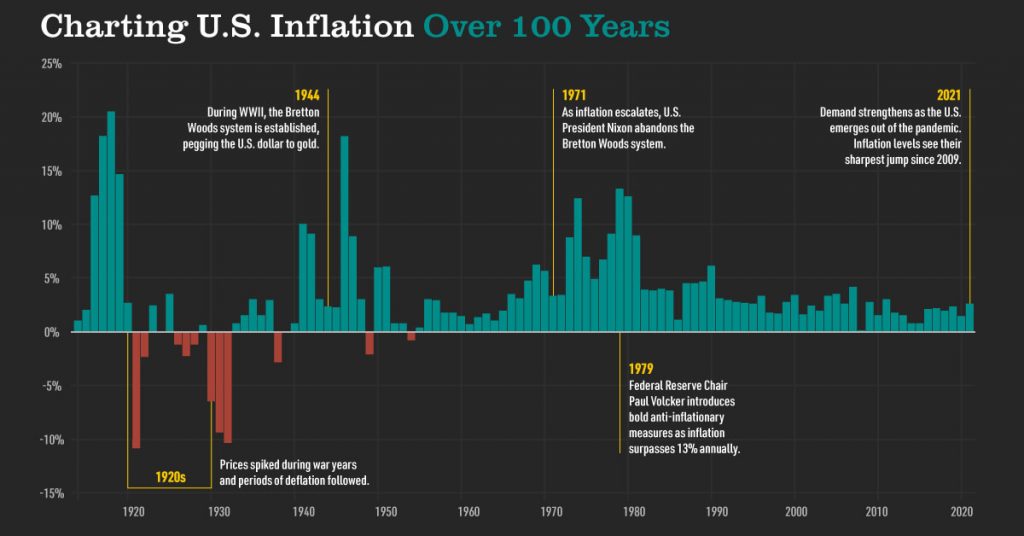
Credit: advisor.visualcapitalist.com
Risk Management Strategies
Risk management strategies consider current and future possibilities, aiming to minimize overall loss while maximizing investment potential. In general, these strategies involve four steps:
Assessing Risk: Current economic conditions, industry sectors, and individual companies must be considered when assessing inflation-related risks. This involves researching past performance, analyzing current trends, and using forecasting tools such as trend analysis and regression analysis to predict possible risks in advance.
Limiting Exposure: Limiting exposure involves putting policies designed to restrict investments or other vulnerabilities in high-risk areas or when inflation could adversely impact market values. Position limits can be used within a portfolio, such as setting a maximum exposure for any single stock within a portfolio or limiting total equity exposure at any time.
Creating Surveillance Systems: Establishing surveillance processes helps identify market behavior changes early, allowing for timely corrective actions. It also provides valuable insights into an Investor’s risk profile, helping future shape activities related to asset allocation or sectoral exposure, among other things.
Monitoring Compliance: Developing robust compliance systems ensures consistent adherence with Investment Guidelines, Portfolio Risk Parameters, Limits, etc., which makes it easier to develop stronger internal controls that help limit exposures while identifying problems quickly if they arise.
Conclusion
In conclusion, while inflation can significantly impact investments, it is still possible to yield positive returns. Through proper evaluation and diversification of assets, investors can effectively minimize the risk associated with inflation.
Inflation-related investment strategies include:
- Investing in inflation-protected treasury securities
- Stocks that pay increasing dividends
- Real estate
- Commodities
Additionally, an investor may be able to hedge against inflationary periods for higher returns with the use of derivatives such as futures and options.
Keeping up with changes in the macroeconomic environment concerning inflation, investors are better equipped to manage the risks associated with their investments actively.



